
#Understanding degrees of freedom how to#
To summarize, Degrees of Freedom are like your ex’s belongings – you must know how many there are and how to get rid of them to move on. Thankfully, not everyone’s ignorance has such terrible consequences. Take NASA scientists for example – their wrong calculations due to inadequate understanding resulted in a $125 million spacecraft crash. Additionally, disregarding this essential concept may lead to flawed data analysis and inaccurate outcomes. When it comes to Degrees of Freedom, remember that sample size requirements are in direct proportion to data reliability. This equates to more overfitting risk and lower accuracy.

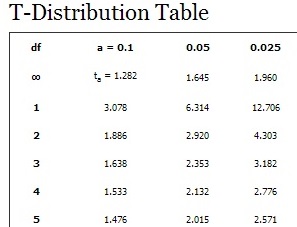
We must recognize that Degrees of Freedom decrease with smaller sample sizes and increased parameters. The variability remaining after accounting for the effect of predictors The difference between the total observations and the regression line The number of means that can vary after estimating an overall mean The number of observations in a sample that can vary after estimating a mean In the table below, we explore several types: Type It’s vital for hypothesis testing and regression analysis, as it helps assess results’ significance.
#Understanding degrees of freedom free#
Definition of Degrees of Freedomĭegrees of Freedom refer to the number of independent and free values in statistical analysis. In order to comprehend the concept of df, definition of degrees of freedom, as well as the importance of degrees of freedom in statistics needs to be explored. To understand degrees of freedom (df) in statistics, you need to delve deeper into its meaning. Therefore, it is essential to assign the right df for reliable statistical deductions.ĭid you know that df was first introduced by Sir Ronald A Fisher in 1925 in his work on ANOVA? Now, let’s go explore the unknown realm of df! Understanding Degrees of Freedom (df) The more variables and parameters, the less df available. For instance, to gauge variance from a sample, use n – 1 df, where n is the sample size.įurthermore, the df count is impacted by the size and complexity of the statistical model. In other words, df signifies the number of independent pieces of knowledge used to calculate a statistical parameter. Degrees of freedom (df) is a mystery to many! It refers to the amount of values or observations in a sample that can alter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
